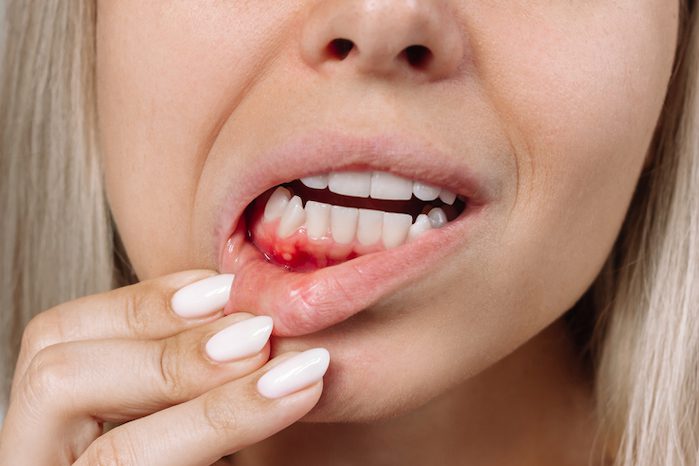
If you notice bleeding from your gums after brushing, it may indicate gum disease, which occurs due to the buildup of plaque on teeth and gums. Early-stage gum disease is called gingivitis, characterized by symptoms such as bleeding gums, redness, and swelling.
If gingivitis progresses without treatment, it can develop into advanced gum disease, known as periodontitis. This stage may lead to more severe symptoms like loose teeth, persistent bad breath, discomfort when biting, and receding gums.
Seeking prompt dental care is crucial if you suspect gum disease. Early treatment not only alleviates symptoms but also helps to preserve your teeth and prevent further complications.
Effective Strategies for Preventing and Treating Bleeding Gums
If you notice signs of gum disease, it’s important to take proactive steps to improve your dental care routine.
Here are effective ways to prevent gum disease and maintain healthy gums:
- brushing. Brush your teeth thoroughly after every meal, spending at least two minutes each time to ensure all surfaces are cleaned;
- flossing. Incorporate daily flossing into your routine to remove plaque and debris from between your teeth and along the gumline. Your dentist or pharmacist can provide guidance on proper flossing techniques;
- soft Toothbrush. If your gums are sensitive or sore, switch to a soft-bristled toothbrush to minimize irritation while cleaning effectively;
- antibacterial Mouthwashes. Consider using antibacterial mouthwashes, available from your pharmacist, to further reduce plaque and bacteria in your mouth. However, it’s advisable to consult with your dentist or pharmacist first, as some mouthwashes may have side effects or interactions;
- professional Advice. Regular dental check-ups are essential. Your dentist can provide personalized advice on maintaining oral health, including proper brushing and flossing techniques tailored to your needs.
By following these steps and seeking guidance from dental professionals, you can effectively prevent gum disease and promote overall oral health. Early intervention and consistent oral care habits are key to avoiding complications and maintaining a healthy smile.
Understanding the Causes and Prevention of Oral Bleeding: From Gum Disease to Other Health Concerns
Mouth bleeding can result from various causes, including physical trauma such as a fall or impact to the face.
Additionally, certain mouth conditions like angular cheilitis and mouth ulcers can lead to bleeding:
- angular Cheilitis. This condition causes cracked, split, and sore lips, often accompanied by pain when opening the mouth. Preventive measures include staying hydrated, using lip balm or ointment regularly, and maintaining good oral hygiene practices;
- mouth Ulcers. These typically resolve on their own but may cause discomfort. You can ask your doctor or pharmacist about topical pain relief ointments.
It’s important to consult your healthcare provider if you experience persistent symptoms such as:
- a sore or ulcer that persists for more than two weeks;
- difficulty swallowing or speaking;
- recurrent bleeding from the mouth;
- red or white patches inside the mouth;
- swelling or numbness in the mouth.
Prompt medical attention ensures proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment for any underlying conditions causing mouth bleeding.
Managing Post-Treatment and Injury-Related Oral Bleeding: Tips and Precautions
Experiencing bleeding after dental treatment or an oral injury is common and often manageable with the right techniques. This guide provides essential tips and precautions to help control bleeding, alleviate discomfort, and promote healing, ensuring you recover quickly and safely.
Bleeding may occur after dental treatment or injury to your teeth and mouth. The following advice can help manage the bleeding and promote healing:
- Apply Pressure. Use gauze to apply pressure over the bleeding area. Alternatively, you can make a pad from a clean, rolled-up cotton handkerchief or other clean cloth. Slightly dampen the pad with clean water before applying.
- Maintain Pressure. Keep the pad in place for 30 minutes without removing it. After this period, check if the bleeding has stopped. If it hasn’t, repeat the process. Continue to apply pressure until you can see a dentist if the bleeding persists.
- Avoid Disturbing the Area. Do not rinse your mouth or put your fingers in your mouth, as this can disrupt clot formation and prolong bleeding.
- Pain Relief. If you experience pain, seek advice on appropriate pain relief medications from your dentist or pharmacist.
- Rest and Diet:
- avoid strenuous activity to prevent exacerbating the bleeding;
- refrain from consuming hot drinks and hard foods. Cold foods like yogurt may be easier to eat and can also provide some pain relief.
- Smoking. Smoking can irritate your mouth and delay healing. If you smoke, try to cut down or quit.
- Follow Dental Advice. Adhere to any specific instructions given by your dentist regarding mouth rinsing, eating, and drinking after dental procedures.
Properly managing post-treatment or injury-related bleeding ensures quicker healing and reduces the risk of complications. If bleeding continues or worsens, seek prompt medical attention.
By following these tips and precautions, you can effectively manage oral bleeding and support the healing process after dental treatments or injuries. Always seek professional advice if bleeding persists or if you experience significant pain. Proper care and timely intervention are key to ensuring a smooth recovery and maintaining oral health.