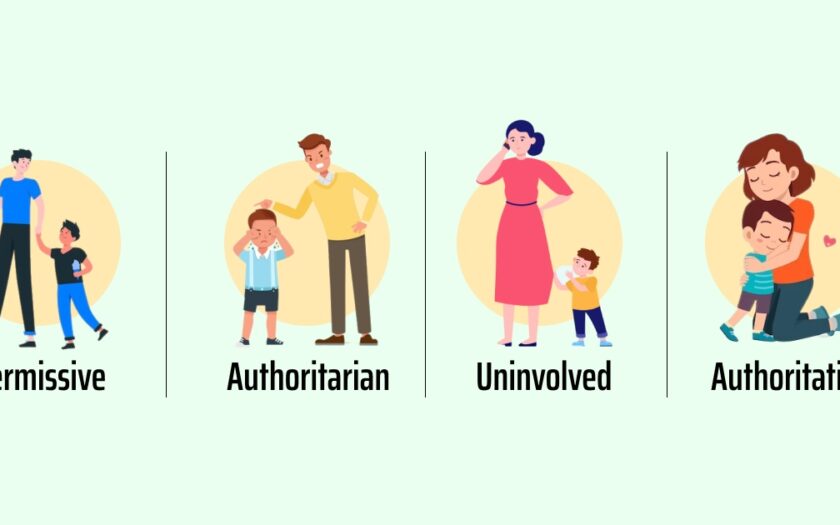
Parenting is undeniably challenging, with numerous decisions and varying opinions on how best to navigate the complexities of raising children. The impact of our parenting choices on our kids adds another layer of pressure. Researchers have delved into this critical and often perplexing subject for years, identifying four primary parenting styles that significantly influence child development and adjustment.
- Authoritative: This parenting style blends high demandingness with high responsiveness. Authoritative parents set clear expectations and rules while being supportive and nurturing. They emphasize independence and self-regulation, fostering open communication and mutual respect.
- Authoritarian: Characterized by high demandingness and low responsiveness, authoritarian parenting prioritizes obedience and discipline. These parents enforce strict rules and consequences, often without much warmth or flexibility in their interactions.
- Permissive: Permissive parents exhibit low demandingness paired with high responsiveness. They are lenient and indulgent, setting few rules and boundaries. These parents are typically warm and nurturing but may struggle to provide structure and guidance.
- Uninvolved: Low demandingness and low responsiveness define uninvolved parenting. These parents are disengaged and offer minimal guidance or support. They may be neglectful or emotionally unavailable, leading to potential challenges in their children’s development.
Each parenting style impacts children differently, influencing their behavior, emotional development, and overall well-being. Understanding your parenting style can provide valuable insights into how you interact with your children and how they may respond to your guidance and support. Balancing warmth and structure while fostering independence and responsibility is key to promoting healthy development in children.
Baumrind’s Parenting Styles
Diana Baumrind, a renowned developmental psychologist from the University of California, Berkeley, introduced the foundational parenting styles in the 1960s through extensive research into parental behaviors and their impacts on children. Her studies initially identified three primary parenting styles, with a fourth added later by researchers Eleanor Maccoby and John Martin.
- Authoritarian Parenting Style: Authoritarian parents are strict and enforce rigid rules with high expectations. They emphasize obedience and conformity, often employing punitive measures when rules are violated without much room for negotiation or explanation.
- Authoritative Parenting Style: Authoritative parents set clear boundaries and expectations but also nurture independence and decision-making skills in their children. They are responsive and supportive, offering guidance and understanding while allowing their children to learn from their mistakes.
- Permissive Parenting Style: Permissive parents are lenient and indulgent, placing few demands on their children. They prioritize responsiveness to their children’s needs and desires over setting strict rules and boundaries. This style often fosters a more friend-like relationship rather than a traditional parent-child dynamic.
- Neglectful Parenting Style: Neglectful parents are uninvolved and indifferent to their children’s needs. They provide little guidance, support, or structure, and may not engage actively in their children’s lives. This lack of responsiveness can lead to negative outcomes for children’s development.
These parenting styles form the basis of much contemporary research on childhood development, offering a spectrum of behaviors that illustrate how parents interact with their children. While every parent-child relationship is unique and dynamic, understanding these styles can help parents reflect on their own approach and its potential impacts on their children’s growth and well-being.
To identify which parenting style resonates most with you, consider your typical responses to your child’s behavior, your approach to setting rules and boundaries, and how you balance warmth and discipline in your interactions. This awareness can guide adjustments in your parenting style to better support your child’s development and overall happiness.
Authoritarian Parenting Style
Authoritarian parenting is characterized by strict adherence to rules and high demands on children to comply without question. Alyson Schafer, a therapist and author specializing in parenting, describes it as a style where parents assert control over their children’s decisions and actions, often with little input or negotiation. Here’s a deeper look into what authoritarian parenting entails and its effects on children:
Description of Authoritarian Parenting: In authoritarian households, parents establish clear rules and expectations that children are expected to follow without deviation. These rules are typically enforced through strict discipline and punitive measures rather than explanations or discussions. Parents maintain authority with an “it’s my way or the highway” approach, emphasizing obedience and conformity to their directives. Decision-making is centralized within the parental domain, and children have limited autonomy or opportunity to express their preferences.
Characteristics of Authoritarian Parenting:
- Strict Rules and Expectations: Authoritarian parents enforce rigid rules that brook no negotiation or deviation. “Because I said so” is a common refrain, emphasizing parental authority over explanations.
- Punishment-Oriented Discipline: Discipline in authoritarian parenting relies heavily on punishments rather than constructive guidance or teaching moments. Consequences are swift and often severe.
- Limited Autonomy: Children have little say in decisions that affect them, such as choices in activities, academics, or personal interests. Decisions are made for them by parents.
- Emotional Distance: Authoritarian parents may prioritize obedience over emotional connection or warmth. Affectionate gestures or emotional support may be less frequent compared to other parenting styles.
Effects of Authoritarian Parenting: Children raised in authoritarian households may exhibit the following tendencies:
- Conformity and Dependence: They are likely to conform to rules and authority figures but may struggle with independent decision-making or critical thinking.
- Difficulty with Self-regulation: Without opportunities to make choices and learn from mistakes, children may struggle with developing their own internal sense of right and wrong.
- Low Self-Esteem: Dependence on external validation and authority can lead to self-esteem issues. Children may seek affirmation from authority figures rather than developing confidence in their own abilities.
- Rebellious Behavior: As children grow older and experience increased autonomy, they may rebel against strict rules and seek alternative sources of guidance or validation.
Understanding the characteristics and effects of authoritarian parenting can help parents reflect on their own approach and consider adjustments that prioritize nurturing independence, fostering open communication, and maintaining supportive relationships with their children.
Authoritative Parenting Style
Authoritative parenting stands out as a balanced and effective approach that combines warmth and support with clear boundaries and expectations. It’s often seen as a middle ground between the strict authoritarian style and the permissive approach. Here’s a closer look at authoritative parenting:
Description of Authoritative Parenting: Authoritative parents set clear and reasonable expectations for their children while also being responsive to their needs. They establish rules and guidelines but allow for flexibility and independence within those boundaries. Communication is open and two-way, with parents explaining the reasons behind rules and decisions and encouraging dialogue.
Characteristics of Authoritative Parenting:
- Clear Expectations with Flexibility: Authoritative parents provide structure and guidelines but allow their children some autonomy to make age-appropriate decisions. Rules are explained and enforced with consistency and fairness.
- Responsive and Supportive: These parents are nurturing and attentive to their children’s emotional and developmental needs. They offer guidance and support while respecting their children’s individuality and encouraging independence.
- Discipline with Explanation: Discipline in authoritative parenting focuses on teaching rather than punishing. Consequences for misbehavior are logical and related to the child’s actions, and parents take the time to explain why certain behaviors are unacceptable.
- Encouragement of Open Communication: Authoritative parents value open communication and encourage their children to express their thoughts and feelings. They listen actively and consider their children’s perspectives in decision-making processes.
Effects of Authoritative Parenting: Research consistently shows that children raised by authoritative parents tend to exhibit positive outcomes, including:
- Confidence and Self-assurance: The supportive and nurturing environment provided by authoritative parents helps children develop a strong sense of self-worth and confidence in their abilities.
- Responsible Decision-making: By allowing children to make choices within structured boundaries, authoritative parenting fosters independence and teaches children how to make responsible decisions.
- Resilience and Problem-solving Skills: Children learn to overcome challenges and setbacks independently, as authoritative parents encourage persistence and provide support when needed.
- Trust in Relationships: The respectful and nurturing relationship between authoritative parents and their children promotes trust and mutual respect, laying a foundation for healthy relationships in the future.
Authoritative parenting is widely regarded as beneficial for children’s emotional and social development, preparing them to navigate challenges and succeed in various aspects of life. Striking a balance between warmth and structure allows children to thrive and grow into capable, confident individuals.
Permissive Parenting Style
Permissive parenting is characterized by a relaxed approach where parents prioritize their children’s desires and happiness over setting strict rules and boundaries. Here’s an overview of what permissive parenting entails and its potential effects on children:
Description of Permissive Parenting: Permissive parents are highly responsive to their children’s immediate wants and needs but are reluctant to enforce consistent rules or impose structure. They often avoid confrontation or setting limits that might be unpopular with their children. This style of parenting is marked by a lack of clear expectations and discipline.
Characteristics of Permissive Parenting:
- Indulgence and Leniency: Permissive parents are indulgent and lenient, allowing their children considerable freedom to make their own choices without interference. They may hesitate to enforce rules or boundaries, preferring to avoid conflict.
- Friendship-oriented Approach: Parents may act more like friends than authority figures, seeking to maintain a close and harmonious relationship with their children rather than asserting leadership or discipline.
- Minimal Structure and Guidance: There is little emphasis on structure or routine within the household. Children may have few responsibilities and may not be held accountable for their actions.
- Avoidance of Confrontation: Permissive parents may avoid confrontations or disagreements with their children, leading to a lack of clear direction or consistent expectations.
Effects of Permissive Parenting: Children raised under permissive parenting may experience various challenges and outcomes:
- Entitlement and Lack of Self-discipline: Without clear boundaries and expectations, children may develop a sense of entitlement and struggle with self-discipline. They may expect immediate gratification and have difficulty delaying gratification.
- Poor Emotional Regulation: The lack of consistent structure and guidance can hinder children’s ability to regulate their emotions effectively. They may struggle with managing frustration, disappointment, or anger.
- Difficulty with Authority: Children may become rebellious or defiant when faced with authority figures or situations that require compliance with rules or norms.
- Risk of Behavioral Issues: In extreme cases, children raised in permissive environments may be more prone to engaging in antisocial behaviors such as substance abuse, delinquency, or risky behaviors.
- Academic and Social Challenges: Without the guidance to develop self-control and responsibility, children may face difficulties in academic settings and struggle to form healthy relationships with peers.
Understanding the characteristics and potential effects of permissive parenting can help parents reflect on their own approach and consider adjustments that promote balanced and healthy development in their children. Balancing warmth and support with appropriate structure and guidance is essential for fostering resilience and positive outcomes in children’s lives.
Neglectful Parenting Style
Neglectful parenting represents a severe lack of engagement and responsiveness from parents towards their children’s needs, which can have profound and lasting effects. Here’s a closer look at neglectful parenting, its characteristics, and the potential consequences for children:
Description of Neglectful Parenting: Neglectful parenting is characterized by a significant lack of involvement and responsiveness from parents towards their children. Unlike other parenting styles, neglectful parents do not set demands or expectations for their children, nor do they provide emotional or physical support. This style of parenting is marked by detachment and minimal interaction with their children’s lives.
Characteristics of Neglectful Parenting:
- Emotional Detachment: Parents show little interest or investment in their children’s emotional well-being. They may be emotionally unavailable, unresponsive to their children’s needs for affection, attention, or guidance.
- Lack of Supervision: Neglectful parents often fail to monitor their children’s activities, behaviors, and whereabouts. There is a lack of parental oversight and involvement in their daily lives.
- Absence of Structure: Children may grow up without clear rules, routines, or boundaries. There is no consistent guidance or direction provided by parents, leaving children to navigate life without parental support.
- Minimal Communication: There is little to no meaningful communication between parents and children. Conversations about feelings, concerns, or important life decisions are rare or nonexistent.
Effects of Neglectful Parenting: Children raised in neglectful environments may face numerous challenges and negative outcomes:
- Attachment Issues: Due to the lack of emotional connection and consistent caregiving, children may struggle to form secure attachments to others. This can impact their ability to develop trusting relationships in childhood and beyond.
- Psychological and Emotional Problems: Neglected children are at higher risk of developing psychological issues such as depression, anxiety, and low self-esteem. They may feel unloved, unwanted, or unworthy due to the absence of nurturing and validation from their parents.
- Behavioral Problems: Without parental guidance and structure, children may exhibit behavioral issues such as aggression, defiance, or delinquency. They may seek attention or validation through negative behaviors or act out due to feelings of neglect or abandonment.
- Social Difficulties: Neglected children may struggle to interact with peers or authority figures appropriately. They may feel isolated or misunderstood, lacking the social skills and emotional resilience needed to navigate social settings.
- Long-term Consequences: The effects of neglectful parenting can extend into adulthood, impacting educational attainment, career success, and overall well-being. Adults who experienced neglect as children may continue to struggle with relationships, parenting their own children, and maintaining stable lifestyles.
Recognizing the signs of neglectful parenting is crucial for early intervention and support. Providing children with consistent care, emotional support, and guidance is essential for their healthy development and well-being. Parents who feel overwhelmed or unable to meet their children’s needs should seek help from trusted professionals or support networks to create a nurturing environment for their children.
What Determines Our Styles of Parenting?
Determining our styles of parenting involves a complex interplay of various factors, including our own upbringing, personal experiences, and individual personality traits. Here’s a closer look at what influences our parenting styles:
- Upbringing and Childhood Experiences: One of the most significant influences on our parenting style is how we were raised ourselves. Parents often model their own parenting techniques after what they experienced growing up. This can involve consciously following the same patterns or, in some cases, actively choosing to parent differently based on what they perceive as effective or lacking in their own upbringing.
- Reaction to Childhood Experiences: Individuals may react to their childhood experiences in different ways when they become parents. For instance, someone who felt overly controlled or restricted by their parents might adopt a more permissive approach to give their own children more freedom and autonomy. Conversely, someone who felt a lack of structure or guidance might lean towards a more authoritative style to provide clear boundaries and support.
- Personality Traits: Our innate personality characteristics play a significant role in shaping how we approach parenting. Personality traits such as assertiveness, conscientiousness, openness to new experiences, and agreeableness can influence the type of parenting style we are inclined to adopt. For example:
- Control vs. Flexibility: Individuals who value control and structure may gravitate towards authoritarian parenting, where rules are strictly enforced. On the other hand, those who prioritize flexibility and openness may lean towards a more permissive style.
- Empathy and Sensitivity: Parents who are highly empathetic and sensitive to their children’s needs may naturally adopt an authoritative style, balancing warmth and responsiveness with clear expectations.
- Belief Systems and Values: Parenting decisions are often guided by personal beliefs, values, and cultural norms. These factors shape our attitudes towards discipline, education, independence, and emotional expression in children. For example, cultural backgrounds may influence whether parents emphasize obedience and respect for authority or encourage individuality and self-expression.
- Parental Goals and Motivations: Each parent has unique goals and motivations for their children’s upbringing. Some may prioritize academic achievement and discipline, while others emphasize emotional intelligence and creativity. These goals influence the strategies parents use to nurture and guide their children towards desired outcomes.
Understanding the factors that shape our parenting styles can help us reflect on our approaches and make intentional decisions about how we interact with and nurture our children. By recognizing the influences of our own upbringing, personality traits, and values, we can strive to create a balanced and supportive environment that promotes our children’s well-being and development.
Dealing With Different Parenting Styles
Dealing with different parenting styles within a family can be both challenging and beneficial. Here’s how to navigate and embrace these differences effectively:
- Recognize and Respect Differences: Understand that each parent may have a unique approach to parenting based on their own upbringing, personality, and beliefs. It’s important to recognize and respect these differences without judgment.
- Avoid Conflict in Front of Children: Children benefit when they see their parents as a united front. Avoid arguing about parenting styles in front of the kids, as this can create confusion and undermine parental authority. Consistency in discipline and expectations is crucial.
- Establish Unified Rules and Expectations: While parents may have different styles, it’s essential to establish common ground on basic rules and expectations for the children. This ensures consistency and clarity in the household.
- Play to Each Parent’s Strengths: Embrace the strengths of each parent’s style. If one parent is better at enforcing bedtime routines, let them take the lead in that area. If another parent excels in teaching patience during homework sessions, capitalize on that strength.
- Communicate and Compromise: Open communication is key to managing parenting differences. Discuss your approaches, understand each other’s perspectives, and find compromises where necessary to ensure both parents feel heard and respected.
- Support Each Other: Parenting is a team effort. Support each other’s decisions even if you may not always agree with every approach. Presenting a united front to your children fosters a sense of security and consistency.
- Celebrate Diversity: Recognize that diversity in parenting styles can enrich children’s experiences by exposing them to different ways of thinking and problem-solving. It teaches them to adapt to various situations and people.
Ultimately, embracing different parenting styles within a family can be an advantage if approached with respect, communication, and a focus on teamwork. By leveraging each parent’s strengths and maintaining consistency in core principles, you can create a supportive and nurturing environment that promotes your children’s growth and well-being.