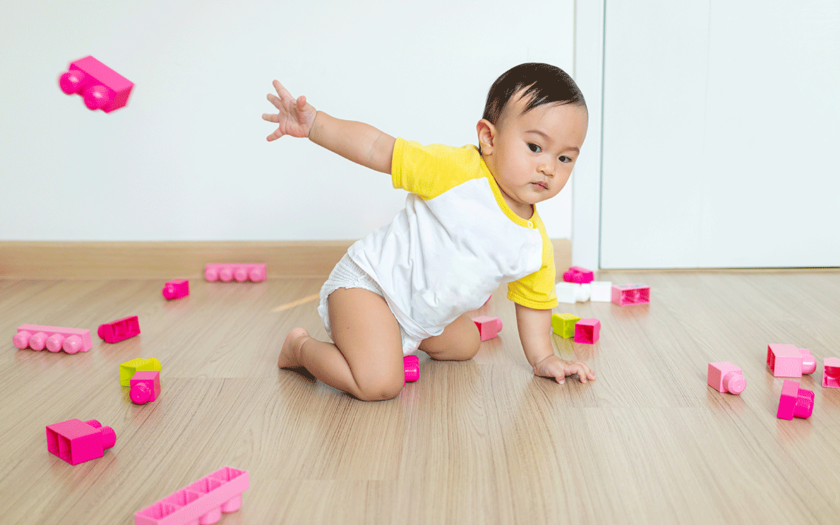
Understanding why toddlers throw things and how to manage this behavior is crucial for parents. Here’s a comprehensive look at the topic:
Why Do Toddlers Throw Things?
- Developmental Milestones: Toddlers typically begin throwing objects intentionally between 12 to 18 months as part of their exploration of cause and effect. This helps them understand concepts like gravity and how objects behave in space.
- Motor Skill Development: Throwing objects supports fine and gross motor skill development, including hand-eye coordination, muscle strength, and motor planning. It’s a form of physical experimentation that aids in their overall physical development.
- Communication and Social Play: For toddlers, throwing can be a way to communicate needs or desires when verbal skills are still developing. It can also be a form of social play, engaging caregivers and eliciting reactions that provide social and language feedback.
- Testing Boundaries: Toddlers may throw objects to test boundaries and observe how caregivers respond, helping them learn about rules and consequences in their environment.
How to Manage Toddler Throwing
- Provide Safe Opportunities: Offer safe objects that are appropriate for throwing, such as soft balls or toys designed for tossing. This redirects their throwing impulses to more acceptable items.
- Model and Teach: Narrate and demonstrate appropriate behaviors. For instance, if a toddler throws food to indicate they’re finished eating, calmly explain and model saying “all done” instead.
- Stay Calm and Neutral: Reacting calmly to throwing incidents helps avoid reinforcing the behavior with attention. If objects are thrown, calmly return them to their place without much reaction.
- Set Clear Boundaries: Establish simple rules about throwing, both indoors and outdoors. Consistently enforce these rules to help toddlers understand expectations.
- Redirect Attention: When toddlers show a desire to throw, redirect their attention to alternative activities or toys that encourage safe play.
- Choose Your Battles: Understand when throwing is developmentally appropriate and when it needs correction. Sometimes, observing cues and understanding the intent behind throwing can guide responses.
- Be Patient and Consistent: Changing behaviors takes time and repetition. Stay patient and provide consistent guidance as toddlers learn and grow.
When Does Throwing Typically Decrease?
Around 24 to 30 months, toddlers often begin to comprehend safety rules better and pick up on social cues. Peer interaction and learning from playing with other children can also influence their understanding of appropriate behavior.
Conclusion
While toddler throwing can be challenging, it’s a normal part of development that supports learning and exploration. By understanding the reasons behind throwing and employing strategies to redirect and teach appropriate behavior, parents can effectively manage this phase while promoting their child’s overall development. Patience, consistency, and a supportive approach are key to guiding toddlers through this exploratory stage.