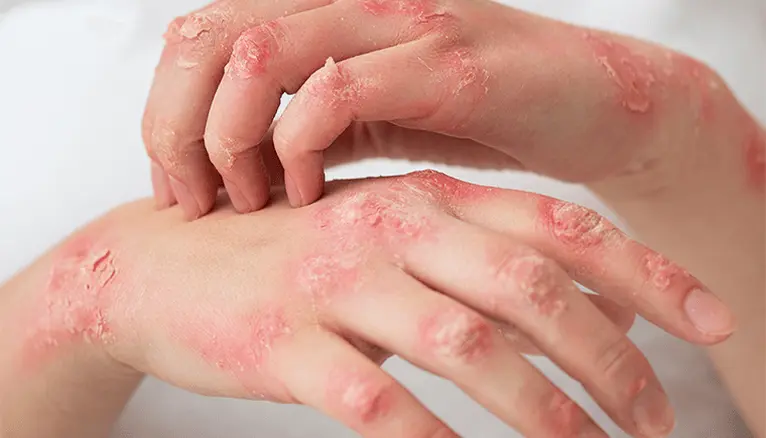
Dermatitis is a term used to describe inflammation of the skin. It encompasses a range of conditions that cause redness, swelling, itching, and sometimes blistering or scaling of the skin. Dermatitis can be acute, meaning it occurs suddenly and lasts for a short period, or it can be chronic, persisting for longer periods or recurring over time.
What are the causes of dermatitis?
Dermatitis is an inflammation of the skin, characterized by changes in the color and structure of the skin. Dermatitis is not contagious and cannot be transmitted from person to person. Causes of dermatitis:
- hereditary predisposition;
- influence of ultraviolet radiation, high or low temperatures;
- skin injuries;
- skin lesions with fungus (candida);
- allergies to medications, food, cosmetics or household chemicals.
Dermatitis can occur due to hormonal changes during pregnancy or menopause, as well as against the background of immunodeficiency (HIV infection). The cause of skin inflammation can be frequent stress and mental stress.
What types of dermatitis?
Dermatitis can be local or diffuse (distributed over the entire surface of the body). There are several types of dermatitis, each with its own causes and symptoms:
- contact dermatitis. This occurs when the skin comes into contact with an irritant or allergen, triggering an inflammatory response. Common irritants include soaps, detergents, cosmetics, certain metals (such as nickel), and chemicals. Allergic contact dermatitis develops when the immune system reacts to an allergen, such as certain plants (e.g., poison ivy), latex, or specific ingredients in skincare products;
- atopic dermatitis (eczema). Atopic dermatitis is a chronic skin condition characterized by dry, itchy skin and often runs in families with a history of allergies or asthma. It can occur at any age but is most common in infants and young children;
- seborrheic dermatitis. Seborrheic dermatitis is a common condition that causes red, scaly patches and dandruff, typically on the scalp, face (particularly around the nose and eyebrows), ears, and chest. It can be exacerbated by stress, weather changes, and certain medical conditions;
- nummular dermatitis. Nummular dermatitis is characterized by round, coin-shaped patches of irritated skin that may be itchy, red, and scaly. The exact cause is unknown, but it may be related to dry skin, irritants, or allergies;
- dyshidrotic dermatitis. Dyshidrotic dermatitis, also known as pompholyx, affects the palms of the hands and soles of the feet, causing small blisters and intense itching. Stress, allergies, and exposure to certain metals are thought to contribute to its development.
Dermatologists also distinguish nervous dermatitis (neurodermatitis), which occurs due to stress or nervous strain, and photodermatitis, which appears due to exposure to sunlight. As a result of wearing synthetic underwear or damage (cracks, diaper rash) to the skin around the anus, anal dermatitis (perianal) develops. In men, if personal hygiene rules are not followed, penile dermatitis may occur.
What should you not eat if you have dermatitis?
If you have dermatitis, you need to eat small meals 5-6 times a day and drink enough fluids. Food should be boiled, baked or steamed.
If you have dermatitis, you should not eat smoked or fried foods, you should also reduce your consumption of allergenic foods (citrus fruits, nuts, fish) and avoid alcoholic beverages.
Skin care for dermatitis in adults and children
If you have dermatitis, you should take a shower daily, the water should be at a moderate temperature (neither hot nor cold). Do not use a washcloth or massage brush.
Skin care for atopic dermatitis in adults and children includes the use of moisturizing and emollient creams or ointments. For weeping dermatitis, it is necessary to use anti-inflammatory and drying drugs; do not smear areas of the skin with alcohol-containing products. When seborrheic dermatitis appears on the head of a child or adult, it is necessary to use hypoallergenic shampoos.
To treat skin inflammation and prevent the development of complications, you must make an appointment with a dermatologist. The use of folk remedies for eczema and dermatitis can lead to the progression of pathology and the development of complications.
How to get rid of dermatitis?
In order to get rid of dermatitis, it is necessary to avoid contact with irritating factors and observe the rules of personal hygiene. For dermatitis, the dermatologist prescribes vitamins (A, group B), anti-inflammatory, antihistamine and steroid (hormonal) drugs.
When treating solar dermatitis, it is necessary to limit exposure to the sun. If children develop atopic dermatitis on their feet, it is necessary to ensure that their feet are clean and that they wear comfortable, appropriately sized shoes. For candidal dermatitis in children and adults, the doctor prescribes antifungal ointments. Treatment for seborrheic dermatitis involves the use of medications that help soften and exfoliate dead skin cells.
How to prevent dermatitis?
Preventing dermatitis involves minimizing exposure to irritants and allergens, maintaining good skin hygiene, and adopting healthy skincare practices. Here are some tips to help prevent dermatitis:
- Identify and avoid triggers. If you know what substances or environmental factors trigger your dermatitis, try to avoid or minimize exposure to them. Common triggers include harsh soaps, detergents, certain metals (like nickel), fragrances, and certain fabrics.
- Use gentle skincare products. Opt for mild, fragrance-free soaps, cleansers, and moisturizers that are formulated for sensitive skin. Avoid products containing harsh chemicals or alcohol, which can strip the skin of its natural oils and exacerbate dermatitis.
- Moisturize regularly. Keep your skin hydrated by applying a moisturizer regularly, especially after bathing or washing your hands. Choose a moisturizer that is hypoallergenic, fragrance-free, and contains ingredients like ceramides or hyaluronic acid to help repair the skin barrier.
- Protect your skin. Wear gloves when working with harsh chemicals or irritants, such as household cleaners or detergents. If you have sensitive skin, consider wearing protective clothing, such as long sleeves and pants, to minimize skin exposure to potential triggers.
- Practice good skincare habits. Take shorter showers with lukewarm water, as hot water can strip the skin of its natural oils and worsen dermatitis. Pat your skin dry gently with a soft towel rather than rubbing vigorously. Avoid scrubbing the skin too harshly, as this can further irritate sensitive skin.
- Manage stress. Stress can exacerbate dermatitis symptoms, so finding ways to manage stress can help prevent flare-ups. Practice relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, yoga, or hobbies that you enjoy.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle. Eating a balanced diet, getting regular exercise, staying hydrated, and getting enough sleep can all contribute to overall skin health and reduce the likelihood of dermatitis flare-ups.
- Seek medical advice. If you develop persistent or severe dermatitis symptoms despite taking preventive measures, consult with a healthcare professional. They can help identify potential triggers, recommend appropriate treatments, and provide personalized advice for managing your condition effectively.
By incorporating these preventive measures into your daily routine and being proactive about managing your skin health, you can reduce the risk of developing dermatitis and minimize flare-ups.